CSGRegion[{reg1,reg2,…}]
represents the solid region corresponding to the union of solid regions reg1,reg2,….
CSGRegion["op",{reg1,reg2,…}]
represents the solid region corresponding to the Boolean combination "op" of regions reg1,reg2,….
CSGRegion["op",{…,wi[regi],…}]
represents the solid region defined by regions regi transformed by a geometric transformation wi.


CSGRegion
CSGRegion[{reg1,reg2,…}]
represents the solid region corresponding to the union of solid regions reg1,reg2,….
CSGRegion["op",{reg1,reg2,…}]
represents the solid region corresponding to the Boolean combination "op" of regions reg1,reg2,….
CSGRegion["op",{…,wi[regi],…}]
represents the solid region defined by regions regi transformed by a geometric transformation wi.
Details and Options



- CSGRegion is also known as constructive solid geometry (CSG) object.
- CSGRegion is typically used to construct solid geometric regions by using nested combinations of union, intersection and subtraction of simple geometric primitives.
- CSGRegion[…] displays in a notebook as a plot of a solid region in 2D and 3D.
- In CSGRegion["op",{reg1,reg2,…}], "op" are Boolean operations and regions regi are other CSGRegion objects or geometric regions.
- The following Boolean operators "op" can be used:
-
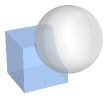
"Intersection" smallest solid containing the intersection of two regions 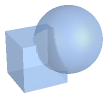
"Difference" smallest solid containing the difference of two regions 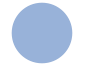
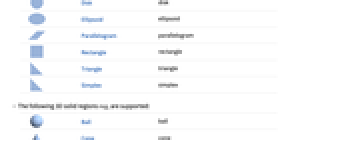
"Union" smallest solid containing the union of two regions - The following 2D solid regions regi are supported:
-
Disk disk 
Ellipsoid ellipsoid 
Parallelogram parallelogram 
Rectangle rectangle 
Triangle triangle 
Simplex simplex - The following 3D solid regions regi are supported:
-

Ball ball 
Cone cone 
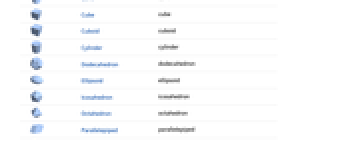
Cube cube 
Cuboid cuboid 
Cylinder cylinder 
Dodecahedron dodecahedron 
Ellipsoid ellipsoid 
Icosahedron icosahedron 
Octahedron octahedron 
Parallelepiped parallelepiped 
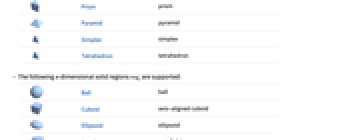
Prism prism 
Pyramid pyramid 
Simplex simplex 
Tetrahedron tetrahedron - The following n‐dimensional solid regions regi are supported:
-

Ball ball 
Cuboid axis-aligned cuboid 
Ellipsoid ellipsoid 
Parallelepiped parallelotope 
Simplex simplex - In CSGRegion["op",{…,wi[regi],…}], wi are geometric transformations or wrappers for regions regi.
- The following geometric transformations wi can be used:
-
GeometricTransformation[regi,…] geometric affine transformation Rotate[regi,…] rotation Scale[regi,…] scaling Translate[regi,…] translation - The following special wrappers wi can be used:
-
Annotation[regi,…] associate an annotation with regi Style[regi,…] show regi with the specified style - CSGRegion[{reg1,reg2,…}] is equivalent to CSGRegion["Union",{reg1,reg2,…}].
- CSGRegion takes the same options as Region.
- CSGRegion can be used with functions such as RegionMember, RegionDistance, RegionMeasure and NIntegrate.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (11)
Basic Uses (4)
Presentation (4)
Annotations (3)
Specify annotations with Annotation:
Check for existing annotations with AnnotationKeys:
Retrieve annotations with AnnotationValue:
Apply annotations with Annotate:
Delete annotations with AnnotationDelete:
Modify annotations with AnnotationValue:
Original CSGRegion gives updated annotation value:
CSGRegion styling is managed through annotations:
Use Style wrapper as a shorthand to specify styling annotations:
Applications (7)
Basic Applications (4)
CSGRegion using multiple operations:
Properties & Relations (4)
Compute the union of two regions:
CSG regions can be represented as Boolean regions:
A CSGRegion object is solid:
The embedding dimension of a CSG region is the same as its geometry dimension:
Possible Issues (1)
CSGRegion with transparency does not show occluded regions:
Use Graphics3D to show all regions:
Interactive Examples (3)
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), CSGRegion, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CSGRegion.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "CSGRegion." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CSGRegion.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). CSGRegion. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CSGRegion.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_csgregion, author="Wolfram Research", title="{CSGRegion}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CSGRegion.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_csgregion, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={CSGRegion}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CSGRegion.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}