ParametricPlot[{fx,fy},{u,umin,umax}]
generates a parametric plot of a curve with x and y coordinates fx and fy as a function of u.
ParametricPlot[{{fx,fy},{gx,gy},…},{u,umin,umax}]
plots several parametric curves.
ParametricPlot[{fx,fy},{u,umin,umax},{v,vmin,vmax}]
plots a parametric region.
ParametricPlot[{{fx,fy},{gx,gy},…},{u,umin,umax},{v,vmin,vmax}]
plots several parametric regions.
ParametricPlot[{…,w[{fx,fy}],…},…]
plots the curve {fx,fy} with features defined by the symbolic wrapper w.
ParametricPlot[…,{u,v}∈reg]
takes parameters {u,v} to be in the geometric region reg.




ParametricPlot
ParametricPlot[{fx,fy},{u,umin,umax}]
generates a parametric plot of a curve with x and y coordinates fx and fy as a function of u.
ParametricPlot[{{fx,fy},{gx,gy},…},{u,umin,umax}]
plots several parametric curves.
ParametricPlot[{fx,fy},{u,umin,umax},{v,vmin,vmax}]
plots a parametric region.
ParametricPlot[{{fx,fy},{gx,gy},…},{u,umin,umax},{v,vmin,vmax}]
plots several parametric regions.
ParametricPlot[{…,w[{fx,fy}],…},…]
plots the curve {fx,fy} with features defined by the symbolic wrapper w.
ParametricPlot[…,{u,v}∈reg]
takes parameters {u,v} to be in the geometric region reg.
Details and Options
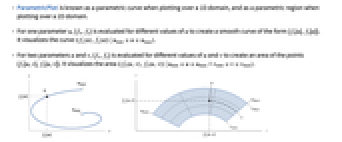





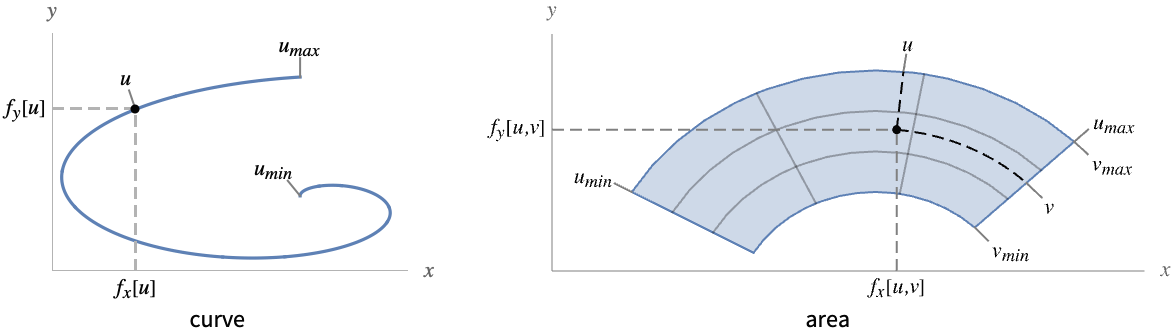
- ParametricPlot is known as a parametric curve when plotting over a 1D domain, and as a parametric region when plotting over a 2D domain.
- For one parameter u, {fx,fy} is evaluated for different values of u to create a smooth curve of the form {fx[u],fy[u]}. It visualizes the curve
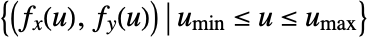 .
. - For two parameters u and v, {fx,fy} is evaluated for different values of u and v to create an area of the points {fx[u,v],fy[u,v]}. It visualizes the area
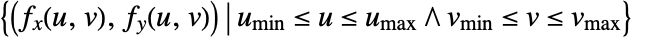 .
. - The curves and regions may intersect or overlap themselves.
- Gaps are left at any u where the fi evaluate to anything other than real numbers.
- The limits umin, umax, vmin and vmax can be real numbers or Quantity expressions.
- The region reg can be any RegionQ object in 1D or 2D.
- ParametricPlot treats the variables u and v as local, effectively using Block.
- ParametricPlot has attribute HoldAll, and evaluates the fi and gi only after assigning specific numerical values to variables.
- In some cases, it may be more efficient to use Evaluate to evaluate the fi and gi symbolically before specific numerical values are assigned to variables.
- Wrappers w can be applied at multiple levels:
-
w[{fx,fy}] wrap {fx,fy} w[{{fx,fy},{gx,gy},…}] wrap a collection of curves w1[w2[…]] use nested wrappers - Callout, Labeled and Placed can use the following positions pos:
-
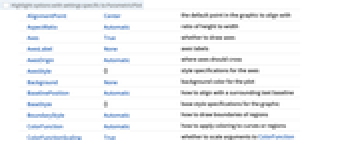
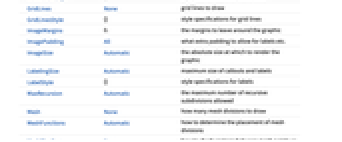
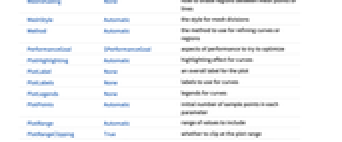
Automatic automatically placed labels Above, Below, Before, After positions around the curve u near the curve at parameter u {x,y} position near {x,y} Scaled[s] scaled position s along the curve {s,Above},{s,Below},… relative position at position s along the curve {pos,epos} epos in label placed at relative position pos of the curve - ParametricPlot has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes True whether to draw axes BoundaryStyle Automatic how to draw boundaries of regions ColorFunction Automatic how to apply coloring to curves or regions ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale arguments to ColorFunction EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate at every function evaluation Exclusions Automatic u points or u, v curves to exclude ExclusionsStyle None what to draw at excluded points or curves Frame Automatic whether to put a frame around the plot LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels MaxRecursion Automatic the maximum number of recursive subdivisions allowed Mesh None how many mesh divisions to draw MeshFunctions Automatic how to determine the placement of mesh divisions MeshShading None how to shade regions between mesh points or lines MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh divisions Method Automatic the method to use for refining curves or regions PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotHighlighting Automatic highlighting effect for curves PlotLabels None labels to use for curves PlotLegends None legends for curves PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points in each parameter PlotRange Automatic range of values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to specify the style for each object PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot RegionFunction (True&) how to determine whether a point should be included ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates TextureCoordinateFunction Automatic how to determine texture coordinates TextureCoordinateScaling True whether to scale arguments to TextureCoordinateFunction WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations - Interactive labeling can be specified for curves and regions using Tooltip, StatusArea, or Annotation.
- ParametricPlot[Tooltip[{{fx,fy},…},…]] specifies that {fx,fy} should be displayed as tooltip labels for the corresponding curves or regions.
- Tooltip[{fx,fy},label] specifies an explicit tooltip label for a curve or region.
- Typical settings for PlotLegends include:
-
None no legend Automatic automatically determine the legend "Expressions" use {fx, fy}, {gx, gy} … as legend labels {lbl1,lbl2,…} use lbl1, lbl2, … as legend labels Placed[lspec,…] specify placement for legend - ColorData["DefaultPlotColors"] gives the default sequence of colors used by PlotStyle.
- ParametricPlot initially evaluates each function at a number of equally spaced sample points specified by PlotPoints. Then it uses an adaptive algorithm to choose additional sample points, subdividing a given interval in each parameter at most MaxRecursion times.
- You should realize that with the finite number of sample points used, it is possible for ParametricPlot to miss features in your functions. To check your results, you should try increasing the settings for PlotPoints and MaxRecursion.
- On[ParametricPlot::accbend] makes ParametricPlot print a message if it is unable to reach a certain smoothness of curve.
- The default setting Mesh->Automatic corresponds to None for curves, and 15 for regions.
- With Mesh->All, ParametricPlot will explicitly draw a point at each sample point on each curve, or will draw a line to indicate each region subdivision.
- The default setting MeshFunctions->Automatic corresponds to {#3&} for curves, and {#3&,#4&} for regions.
- The arguments supplied to functions in MeshFunctions and RegionFunction are x, y, u, and v. Functions in ColorFunction and TextureCoordinateFunction are by default supplied with scaled versions of these arguments.
- The functions are evaluated all along each curve, or all over each region.
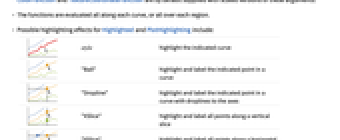
- Possible highlighting effects for Highlighted and PlotHighlighting include:
-
style highlight the indicated curve 
"Ball" highlight and label the indicated point in a curve 
"Dropline" highlight and label the indicated point in a curve with droplines to the axes 
"XSlice" highlight and label all points along a vertical slice 
"YSlice" highlight and label all points along a horizontal slice 
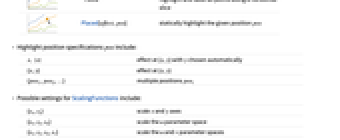
Placed[effect,pos] statically highlight the given position pos - Highlight position specifications pos include:
-
x, {x} effect at {x,y} with y chosen automatically {x,y} effect at {x,y} {pos1,pos2,…} multiple positions posi - Possible settings for ScalingFunctions include:
-
{sx,sy} scale x and y axes {sx,sy,su} scale the u parameter space {sx,sy,su,sv} scale the u and v parameter spaces - Common built-in scaling functions s include:
-
"Log" 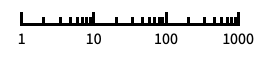
log scale with automatic tick labeling "Log10" 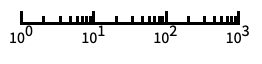
base-10 log scale with powers of 10 for ticks "SignedLog" 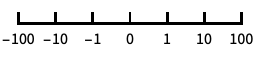
log-like scale that includes 0 and negative numbers "Reverse" 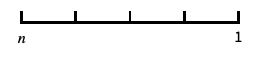
reverse the coordinate direction "Infinite" 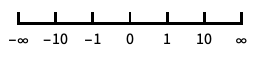
infinite scale - Scaling the u or v parameter space affects how the plot is sampled, but not the overall visual appearance of the plot.
- ParametricPlot returns Graphics[Line[data]] for curves and Graphics[GraphicsComplex[data]] for regions.
-
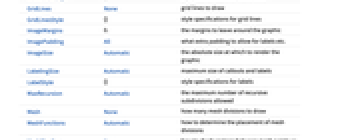
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes True whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic BoundaryStyle Automatic how to draw boundaries of regions ColorFunction Automatic how to apply coloring to curves or regions ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale arguments to ColorFunction ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot EvaluationMonitor None expression to evaluate at every function evaluation Exclusions Automatic u points or u, v curves to exclude ExclusionsStyle None what to draw at excluded points or curves FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame Automatic whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels MaxRecursion Automatic the maximum number of recursive subdivisions allowed Mesh None how many mesh divisions to draw MeshFunctions Automatic how to determine the placement of mesh divisions MeshShading None how to shade regions between mesh points or lines MeshStyle Automatic the style for mesh divisions Method Automatic the method to use for refining curves or regions PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotHighlighting Automatic highlighting effect for curves PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotLabels None labels to use for curves PlotLegends None legends for curves PlotPoints Automatic initial number of sample points in each parameter PlotRange Automatic range of values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to specify the style for each object PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RegionFunction (True&) how to determine whether a point should be included RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates TextureCoordinateFunction Automatic how to determine texture coordinates TextureCoordinateScaling True whether to scale arguments to TextureCoordinateFunction Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks WorkingPrecision MachinePrecision the precision used in internal computations
List of all options


Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (34)
Sampling (9)
More points are sampled when the function changes quickly:
The plot range is selected automatically:
Ranges where the function becomes nonreal are excluded:
The curve is split when there are discontinuities in the function:
Use PlotPoints and MaxRecursion to control adaptive sampling:
Use PlotRange to focus in on areas of interest:
Use Exclusions to remove points or split the resulting curve:
The domain of the parameters may be specified by a region:
The domain of the parameters may be specified by a MeshRegion:
Labeling and Legending (13)
Use Callout to add the expressions as a label:
Place the label along the curve:
Place the label at a scaled position:
Place the labels relative to the inside of the curve:
Place the labels relative to the outside of the curve:
Place the label inside a region:
Label the curve with PlotLabels:
Specify the text position relative to the point:
Specify the label at {x,y} position:
Place the label outside of a region:
Include legends for each curve:
Include legends for each region:
Use Legended to provide a legend for a specific curve:
Use Placed to change the legend location:
Curves usually have interactive callouts showing the coordinates when you mouse over them:
Including specific wrappers or interactions, such as tooltips, turns off the interactive features:
Choose from multiple interactive highlighting effects:
Use Highlighted to emphasize specific points in a plot:
Presentation (12)
Multiple curves and regions are automatically colored to be distinct:
Identify curves and regions with legends:
Provide explicit styling to different curves and regions:
Provide an interactive Tooltip for each curve or region:
Style the areas between mesh levels:
Reverse the direction of the x axis:
Scale u space parameter to affect sampling, but not the general shape:
Options (88)
BoundaryStyle (3)
Use a red boundary around the edges of the surface:
BoundaryStyle applies to regions cut by RegionFunction:
BoundaryStyle does not apply to holes cut by Exclusions:
ColorFunction (5)
Color the curve by scaled ![]() ,
, ![]() , or
, or ![]() values:
values:
Color by scaled ![]() and
and ![]() parameter values:
parameter values:
ColorFunction has higher priority than PlotStyle:
ColorFunctionScaling (2)
EvaluationMonitor (3)
Exclusions (5)
ExclusionsStyle (3)
LabelingSize (2)
MaxRecursion (2)
Each level of MaxRecursion will adaptively subdivide the initial mesh into a finer mesh:
Mesh (5)
MeshFunctions (3)
MeshShading (7)
Alternate red and blue arcs in the ![]() direction:
direction:
Use None to remove segments:
MeshShading can be used with PlotStyle:
MeshShading has higher priority than PlotStyle for styling:
Use PlotStyle for some segments by setting MeshShading to Automatic:
MeshShading can be used with ColorFunction:
MeshStyle (4)
PerformanceGoal (2)
PlotHighlighting (8)
Plots have interactive coordinate callouts with the default setting PlotHighlightingAutomatic:
Use PlotHighlightingNone to disable the highlighting for the entire plot:
Use Highlighted[…,None] to disable highlighting for a single curve:
Move the mouse over the curve to highlight it with a ball and label:
Use a ball and label to highlight parts that match specific points on the curve:
Move the mouse over the curve to highlight it with a label and droplines to the axes:
Use a ball and label to highlight a specific point on the curve:
Move the mouse over the plot to highlight it with a slice showing ![]() values corresponding to the
values corresponding to the ![]() position:
position:
Highlight the curves at a fixed ![]() value:
value:
Move the mouse over the plot to highlight it with a slice showing ![]() values corresponding to the
values corresponding to the ![]() position:
position:
Use a component that shows the points on the curve closest to the ![]() position of the mouse cursor:
position of the mouse cursor:
Specify the style for the points:
Use a component that shows the coordinates on the curve closest to the mouse cursor:
Use Callout options to change the appearance of the label:
PlotLabels (6)
Specify the text to label the curves:
Place the labels above the curves:
Place the labels differently for each curve:
PlotLabels->"Expressions" uses functions as curve labels:
Use callouts to identify the curves:
Put labels relative to the outside of the curves:
Use None to not add a label:
PlotLegends (7)
No legends are used by default:
Create a legend based on the functions:
Create a legend with placeholder text:
Create a legend with specific labels:
PlotLegends picks up PlotStyle values automatically:
Use Placed to position legends:
Use LineLegend to modify the appearance of the legend:
PlotPoints (2)
PlotRange (2)
With the natural range of values, the fine detail around the origin is not visible:
Use PlotRange to focus in on areas of interest:
PlotStyle (4)
Use different style directives:
By default different styles are chosen for multiple curves and regions:
Explicitly specify the style for different curves and regions:
PlotStyle can be combined with ColorFunction:
PlotTheme (2)
ScalingFunctions (3)
By default, ParametricPlot uses a natural scale:
Use a sign-aware log scale for the y axis:
Use ScalingFunctions to reverse the direction of axes:
TextureCoordinateFunction (4)
Applications (9)
Simple parametric curves including a line:
Simple parametric regions including a rectangle:
Plot a whole family of rotated ellipses:
Different parametrizations of circles:
This rational parametrization is for ![]() :
:
Make a phase space plot of a solution to the Lotka–Volterra predator-prey equations:
Properties & Relations (7)
Plot is a special case of ParametricPlot for curves:
PolarPlot is a special case of ParametricPlot for curves:
Use ListPlot and ListLinePlot for data:
Use ContourPlot and RegionPlot for implicit curves and regions:
Use LogPlot, LogLinearPlot, and LogLogPlot for logarithmic plots:
Use Plot3D and ParametricPlot3D for function and parametric surfaces:
Use RevolutionPlot3D and SphericalPlot3D for cylindrical and spherical coordinates:
Possible Issues (1)
By default, the argument is not evaluated and is styled as one composite function:
Use Evaluate to get an explicit list of curves:
See Also
PolarPlot ContourPlot RegionPlot Plot StreamPlot ParametricPlot3D ComplexPlot Graphics
Function Repository: DirectionParametricPlot ApproximatedCurve CurvatureTorsionPlot3D
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2010 (8.0) ▪ 2012 (9.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2022 (13.1) ▪ 2023 (13.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), ParametricPlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParametricPlot.html (updated 2023).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "ParametricPlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2023. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParametricPlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). ParametricPlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParametricPlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_parametricplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ParametricPlot}", year="2023", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParametricPlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_parametricplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ParametricPlot}, year={2023}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParametricPlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}