GeoListPlot[{loc1,loc2,…}]
generates a map on which the locations loci are indicated.
GeoListPlot[{list1,list2,…}]
generates a map showing several lists of locations.




GeoListPlot
GeoListPlot[{loc1,loc2,…}]
generates a map on which the locations loci are indicated.
GeoListPlot[{list1,list2,…}]
generates a map showing several lists of locations.
Details and Options




- The geographic locations loci can be given in the following forms:
-
GeoPosition[{lat,lon}] latitude and longitude Entity[…] geographic entity Dated[ent,date] dated entity GeoGroup[{…}] grouped set of entities Polygon,GeoDisk,… geographic regions - Multiple locations locs can be given in the following forms:
-
{loc1,loc2,…} list of individual locations GeoPosition[{pos1,pos2,…}] array of geo positions EntityClass[…] class of geo entities - The data datai for GeoListPlot can be given in the following forms:
-
{e1,e2,…} list of elements with or without wrappers <|k1e1,k2e2,…|> association of keys and values WeightedData[…] positions with weights for values w[{e1,e2,…},…] wrapper applied to a whole dataset w[{data1,data1,…},…] wrapper applied to all datasets - The following wrappers can be used for map elements:
-
Annotation[e,label] provide an annotation Button[e,action] define an action to execute when the element is clicked EventHandler[e,…] define a general event handler for the element Hyperlink[e,uri] make the element act as a hyperlink Labeled[e,…] display the element with labeling Legended[e,…] include features of the element in a chart legend PopupWindow[e,cont] attach a popup window to the element StatusArea[e,label] display in the status area when the element is moused over Style[e,opts] show the element using the specified styles Tooltip[e,label] attach an arbitrary tooltip to the element - Data not given in these forms is ignored in forming the plot.
- GeoListPlot takes the same options as GeoGraphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
GeoLabels None whether to label locations with their names Joined False whether to join consecutive locations LabelStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine style of labels PlotLegends Automatic legends for data PlotMarkers Automatic how to mark locations PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine style of the loci - The following settings for GeoLabels can be used:
-
Automatic add text labels to graphical output None add no labels func apply the function func - PlotMarkers can take the following forms:
-
Automatic automatically chosen plot markers Polygon use polygons Point use points GeoMarker use geo markers "OpenMarkers" open shapes g markers consisting of copies of expression g {g,s} expression g at size s {Automatic,spec} automatic marker with fallback spec {Polygon,spec} polygon with fallback spec {spec1,spec2,…} plot marker specifications for data1, data2, … - With PlotMarkers -> Automatic, polygons are used to show entity regions. A point will be used instead if the polygon is too small compared to the overall map, or if no polygon is available.
- The arguments supplied to functions in GeoLabels are graphicsi, regi, and EntityValue[regi,"Position"], where graphicsi is the Graphics or GeoGraphics object that marks regi, by default either a Point or a Polygon.
-
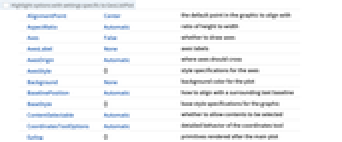
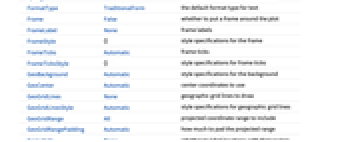
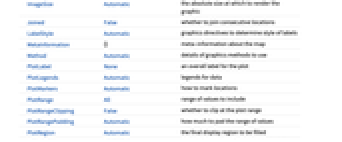
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio Automatic ratio of height to width Axes False whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame False whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GeoBackground Automatic style specifications for the background GeoCenter Automatic center coordinates to use GeoGridLines None geographic grid lines to draw GeoGridLinesStyle Automatic style specifications for geographic grid lines GeoGridRange All projected coordinate range to include GeoGridRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the projected range GeoLabels None whether to label locations with their names GeoModel Automatic model of the Earth (or other body) to use GeoProjection Automatic projection to use GeoRange Automatic geographic area range to include GeoRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the geographic range GeoResolution Automatic average distance between background pixels GeoScaleBar None scale bar to display GeoServer Automatic specification of a tile server GeoZoomLevel Automatic zoom to use for geographic background GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic Joined False whether to join consecutive locations LabelStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine style of labels MetaInformation {} meta-information about the map Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use PlotLabel None an overall label for the plot PlotLegends Automatic legends for data PlotMarkers Automatic how to mark locations PlotRange All range of values to include PlotRangeClipping False whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine style of the loci PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RasterSize Automatic raster dimensions for the background data RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks
List of all options

Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (5)
Display multiple lists of locations:
On large scales, cities and other small locations are marked by points:
GeoListPlot works with most geographic entities and GeoPosition:
GeoListPlot works with annotated locations:
GeoListPlot works with TemporalData, TimeSeries, and EventSeries, such as the main landings of the first voyage of Columbus:
Options (44)
AspectRatio (4)
By default, the ratio of the height to width for the plot is determined automatically:
Make the height the same as the width with AspectRatio1:
Use numerical value to specify the height-to-width ratio:
AspectRatioFull adjusts the height and width to tightly fit inside other constructs:
Axes (4)
By default, Axes are not drawn for maps:
Use AxesTrue to turn on axes:
Axes show GeoGridPosition coordinates for the projection instead of latitude and longitude:
AxesOrigin (2)
AxesStyle (4)
Frame (4)
GeoListPlot does not use a frame by default:
Use FrameTrue to draw a frame around the plot:
FrameLabel (4)
GeoLabels (2)
ImageSize (4)
Use named sizes such as Tiny, Small, Medium and Large:
Specify the width of the plot:
Specify the height of the plot:
Specify the width and height for a graphic, padding with space if necessary:
Setting AspectRatioFull will fill the available space:
Use ImageSizeFull to fill the available space in an object:
Joined (3)
By default, GeoListPlot uses geodesics given by GeoPath to join locations:
Join location data from a TimeSeries or EventSeries in temporal order:
LabelStyle (2)
PlotMarkers (3)
Use a default sequence of shapes to distinguish sets of locations:
Mark every location with points:
Use a GeoMarker to mark cities:
Applications (1)
Plot locations of strong earthquakes given by an EventSeries:
Properties & Relations (8)
Use GeoBubbleChart to show values with scaled bubbles:
Use GeoRegionValuePlot to show values with colored regions:
Use GeoHistogram to aggregate locations into bins:
Use GeoSmoothHistogram to generate smooth densities from locations:
Use GeoVectorPlot and GeoStreamPlot for vector fields:
Draw contours on a map with GeoContourPlot:
Smoothly shade a map using color with GeoDensityPlot:
Neat Examples (2)
Explore solutions to the traveling salesman problem for South America:
Use WolframAlpha to highlight the countries with the highest population:
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), GeoListPlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoListPlot.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "GeoListPlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoListPlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). GeoListPlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoListPlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_geolistplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GeoListPlot}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoListPlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_geolistplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GeoListPlot}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GeoListPlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}