Search for all pages containing ListPlot
- See Also
-
Related Guides
- Data Visualization
- GPU Computing
- Numbers with Uncertainty
- Tabular Visualization
- Discrete Calculus
- Charting and Information Visualization
- Scientific Data Analysis
- Tabular Processing Overview
- Tabular Communication
- Signal Visualization & Analysis
- Handling Arrays of Data
- GPU Computing with NVIDIA
- GPU Computing with Apple
- Statistical Visualization
- Numerical Data
- Financial Visualization
- Function Visualization
- Associations
- Spatial Point Collections
- Probability & Statistics with Quantities
- Audio Representation
- Workflows
- Tech Notes
-
- See Also
-
Related Guides
- Data Visualization
- GPU Computing
- Numbers with Uncertainty
- Tabular Visualization
- Discrete Calculus
- Charting and Information Visualization
- Scientific Data Analysis
- Tabular Processing Overview
- Tabular Communication
- Signal Visualization & Analysis
- Handling Arrays of Data
- GPU Computing with NVIDIA
- GPU Computing with Apple
- Statistical Visualization
- Numerical Data
- Financial Visualization
- Function Visualization
- Associations
- Spatial Point Collections
- Probability & Statistics with Quantities
- Audio Representation
- Workflows
- Tech Notes




ListPlot
Details and Options











- ListPlot is also known as a scatter plot or point plot when given a list of heights yi.
- Regular data {y1,…,yn} is plotted as the points {i,yi}.
- Irregular data {{x1,y1},…,{xn,yn}} is plotted as points {xi,yi}.
- Data values xi and yi can be given in the following forms:
-
xi a real-valued number Quantity[xi,unit] a quantity with a unit Around[xi,ei] value xi with uncertainty ei Interval[{xmin,xmax}] values between xmin and xmax - Values xi and yi that are not of the form above are taken to be missing and are not shown.
- The datai have the following forms and interpretations:
-
<|"k1"y1,"k2"y2,…|> values {y1,y2,…} <|x1y1,x2y2,…|> key-value pairs {{x1,y1},{x2,y2},…} {y1"lbl1",y2"lbl2",…}, {y1,y2,…}{"lbl1","lbl2",…} values {y1,y2,…} with labels {lbl1,lbl2,…} SparseArray values as a normal array TimeSeries, EventSeries time-value pairs QuantityArray magnitudes WeightedData unweighted values - ListPlot[Tabular[…]cspec] extracts and plots values from the tabular object using the column specification cspec.
- The following forms of column specifications cspec are allowed for plotting tabular data:
-
{colx,coly} plot column y against column x {{colx1,coly1},{colx2,coly2},…} plot column y1 against column x1, y2 against x2, … coly, {coly} plot column y as a sequence of values {{coly1},…,{colyi},…} plot columns y1, y2, … as sequences of values - The colx can also be Automatic, in which case, sequential values are generated using DataRange.
- The following wrappers w can be used for the datai:
-
Annotation[datai,label] provide an annotation for the data Button[datai,action] define an action to execute when the data is clicked Callout[datai,label] label the data with a callout Callout[datai,label,pos] place the callout at relative position pos EventHandler[datai,…] define a general event handler for the data Highlighted[datai,effect] dynamically highlight fi with an effect Highlighted[datai,Placed[effect,pos]] statically highlight fi with an effect at position pos Hyperlink[datai,uri] make the data a hyperlink Labeled[datai,label] label the data Labeled[datai,label,pos] place the label at relative position pos Legended[datai,label] identify the data in a legend PopupWindow[datai,cont] attach a popup window to the data StatusArea[datai,label] display in the status area on mouseover Style[datai,styles] show the data using the specified styles Tooltip[datai,label] attach a tooltip to the data Tooltip[datai] use data values as tooltips - Wrappers w can be applied at multiple levels:
-
{…,w[yi],…} wrap the value yi in data {…,w[{xi,yi}],…} wrap the point {xi,yi} w[datai] wrap the data w[{data1,…}] wrap a collection of datai w1[w2[…]] use nested wrappers - Callout, Labeled, and Placed can use the following positions pos:
-
Automatic automatically placed labels 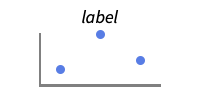
Above positions above data or point 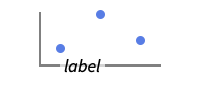
Below positions below data or point 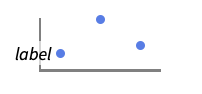
Before positions before data or point 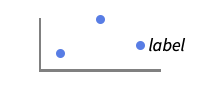
After positions after data or point 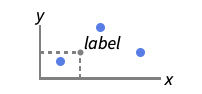
{pos,epos} epos in label placed at relative position pos of the data - ListPlot has the same options as Graphics, with the following additions and changes: [List of all options]
-
AspectRatio 1/GoldenRatio ratio of height to width Axes True whether to draw axes ColorFunction Automatic how to determine the coloring of points ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale data to ColorFunction DataRange Automatic the range of x values to assume for data IntervalMarkers Automatic how to render uncertainty IntervalMarkersStyle Automatic style for uncertainty elements Filling None how to fill in stems for each point FillingStyle Automatic style to use for filling Joined False whether to join points LabelingFunction Automatic how to label points LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels LabelingTarget Automatic how to determine automatic label positions MultiaxisArrangement None how to arrange multiple axes for data PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotFit None how to fit a curve to the points PlotFitElements Automatic fitted elements to show in the plot PlotHighlighting Automatic highlighting effect for curves PlotInteractivity $PlotInteractivity whether to allow interactive elements PlotLabel None overall label for the plot PlotLabels None labels for data PlotLayout "Overlaid" how to position data PlotLegends None legends for data PlotMarkers None markers to use to indicate each point PlotRange Automatic range of values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine styles of points PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates TargetUnits Automatic units to display in the plot - DataRange determines how values {y1,…,yn} are interpreted into {{x1,y1},…,{xn,yn}}. Possible settings include:
-
Automatic,All uniform from 1 to n {xmin,xmax} uniform from xmin to xmax - In general a list of pairs {{x1,y1},{x2,y2},…} is interpreted as a list of points, but the setting DataRangeAll forces it to be interpreted as multiple datai {{y11,y12},{y21,y23},…}. »
- LabelingFunction->f specifies that each point should have a label given by f[value,index,lbls], where value is the value associated with the point, index is its position in the data, and lbls is the list of relevant labels.
- Possible settings for PlotLayout that show multiple curves in a single plot panel include:
-
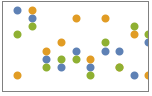
"Overlaid" show all the data overlapping 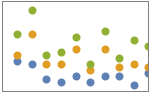
"Stacked" accumulate the data 
"Percentile" accumulate and normalize the data - Possible settings for PlotLayout that show single curves in multiple plot panels include:
-
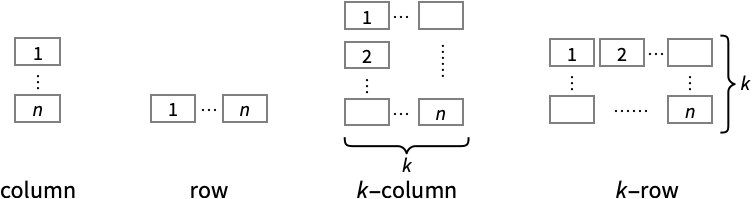
"Column" use separate plots in a column of panels "Row" use separate plots in a row of panels {"Column",k},{"Row",k} use k columns or rows {"Column",UpTo[k]},{"Row",UpTo[k]} use at most k columns or rows - Possible highlighting effects for Highlighted and PlotHighlighting include:
-
style highlight the indicated data 
"Ball" highlight and label the indicated point in data 
"Dropline" highlight and label the indicated point in data with droplines to the axes 
"XSlice" highlight and label all points along a vertical slice 
"YSlice" highlight and label all points along a horizontal slice 
Placed[effect,pos] statically highlight the given position pos - Highlight position specifications pos include:
-
x, {x} effect at {x,y} with y chosen automatically {x,y} effect at {x,y} {pos1,pos2,…} multiple positions posi - Typical settings for PlotLegends include:
-
None no legend Automatic automatically determine legend {lbl1,lbl2,…} use lbl1, lbl2, … as legend labels Placed[lspec,…] specify placement for legend - ColorData["DefaultPlotColors"] gives the default sequence of colors used by PlotStyle.
- ScalingFunctions->"scale" scales the
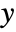 coordinate; ScalingFunctions{"scalex","scaley"} scales both the
coordinate; ScalingFunctions{"scalex","scaley"} scales both the 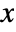 and
and 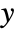 coordinates.
coordinates. - The arguments supplied to functions in ColorFunction are
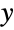 and
and 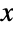 . Functions in ColorFunction are by default supplied with scaled versions of these arguments.
. Functions in ColorFunction are by default supplied with scaled versions of these arguments. -
 Highlight options with settings specific to ListPlot
Highlight options with settings specific to ListPlot
-
AlignmentPoint Center the default point in the graphic to align with AspectRatio 1/GoldenRatio ratio of height to width Axes True whether to draw axes AxesLabel None axes labels AxesOrigin Automatic where axes should cross AxesStyle {} style specifications for the axes Background None background color for the plot BaselinePosition Automatic how to align with a surrounding text baseline BaseStyle {} base style specifications for the graphic ColorFunction Automatic how to determine the coloring of points ColorFunctionScaling True whether to scale data to ColorFunction ContentSelectable Automatic whether to allow contents to be selected CoordinatesToolOptions Automatic detailed behavior of the coordinates tool DataRange Automatic the range of x values to assume for data Epilog {} primitives rendered after the main plot Filling None how to fill in stems for each point FillingStyle Automatic style to use for filling FormatType TraditionalForm the default format type for text Frame False whether to put a frame around the plot FrameLabel None frame labels FrameStyle {} style specifications for the frame FrameTicks Automatic frame ticks FrameTicksStyle {} style specifications for frame ticks GridLines None grid lines to draw GridLinesStyle {} style specifications for grid lines ImageMargins 0. the margins to leave around the graphic ImagePadding All what extra padding to allow for labels etc. ImageSize Automatic the absolute size at which to render the graphic IntervalMarkers Automatic how to render uncertainty IntervalMarkersStyle Automatic style for uncertainty elements Joined False whether to join points LabelingFunction Automatic how to label points LabelingSize Automatic maximum size of callouts and labels LabelingTarget Automatic how to determine automatic label positions LabelStyle {} style specifications for labels Method Automatic details of graphics methods to use MultiaxisArrangement None how to arrange multiple axes for data PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal aspects of performance to try to optimize PlotFit None how to fit a curve to the points PlotFitElements Automatic fitted elements to show in the plot PlotHighlighting Automatic highlighting effect for curves PlotInteractivity $PlotInteractivity whether to allow interactive elements PlotLabel None overall label for the plot PlotLabels None labels for data PlotLayout "Overlaid" how to position data PlotLegends None legends for data PlotMarkers None markers to use to indicate each point PlotRange Automatic range of values to include PlotRangeClipping True whether to clip at the plot range PlotRangePadding Automatic how much to pad the range of values PlotRegion Automatic the final display region to be filled PlotStyle Automatic graphics directives to determine styles of points PlotTheme $PlotTheme overall theme for the plot PreserveImageOptions Automatic whether to preserve image options when displaying new versions of the same graphic Prolog {} primitives rendered before the main plot RotateLabel True whether to rotate y labels on the frame ScalingFunctions None how to scale individual coordinates TargetUnits Automatic units to display in the plot Ticks Automatic axes ticks TicksStyle {} style specifications for axes ticks
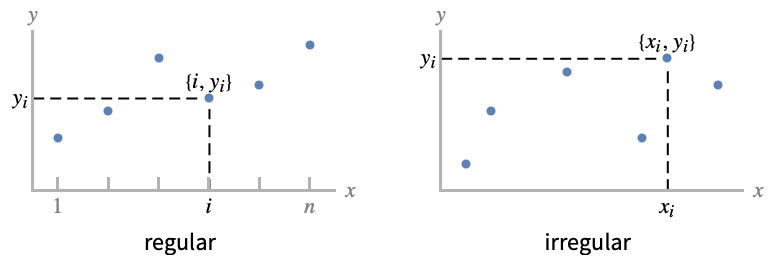
List of all options
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (7)
Scope (60)
General Data (11)
For regular data consisting of ![]() values, the
values, the ![]() data range is taken to be integer values:
data range is taken to be integer values:
Provide an explicit ![]() data range by using DataRange:
data range by using DataRange:
Plot multiple sets of regular data:
For irregular data consisting of ![]() value pairs, the
value pairs, the ![]() data range is inferred from data:
data range is inferred from data:
Plot multiple sets of irregular data:
Plot multiple sets of data, regular or irregular, using DataRange to map them to the same ![]() range:
range:
Ranges where the data is nonreal are excluded:
Use MaxPlotPoints to limit the number of points used:
PlotRange is selected automatically:
Use PlotRange to focus on areas of interest:
Use ScalingFunctions to scale the axes:
Tabular Data (1)
Plot sepal widths against sepal lengths:
Use PivotToColumns to create columns of sepal length for each species:
Plot petal length against width for each of the species of iris:
Use abbreviated names for extended keys when the elements are unique:
Special Data (9)
Use Quantity to include units with the data:
Include different units for the x and y coordinates:
Plot data in a QuantityArray:
Specify the units used with TargetUnits:
Specify strings to use as labels:
Specify a location for labels:
Numeric values in an Association are used as the ![]() coordinates:
coordinates:
Numeric keys and values in an Association are used as the ![]() and
and ![]() coordinates:
coordinates:
Plot TimeSeries directly with automatic date ticks:
Plot data in a SparseArray:
The weights in WeightedData are ignored:
Data Wrappers (6)
Use wrappers on individual data, datasets, or collections of datasets:
Use the value of each point as a tooltip:
Use a specific label for all the points:
Labels points with automatically positioned text:
Use PopupWindow to provide additional drilldown information:
Button can be used to trigger any action:
Labeling and Legending (16)
Label points with automatically positioned text:
Place the labels relative to the points:
Label data with Labeled:
Label data with PlotLabels:
Place the label near the points at a x value:
Specify the text position relative to the point:
Label data automatically with Callout:
Place a label with a specific location:
Specify label names with LabelingFunction:
Specify the maximum size of labels:
For dense sets of points, some labels may be turned into tooltips by default:
Increasing the size of the plot will show more labels:
Include legends for each curve:
Use Legended to provide a legend for a specific dataset:
Use Placed to change the legend location:
Use association keys as labels:
Plots usually have interactive callouts showing the coordinates when you mouse over them:
Including specific wrappers or interactions, such as tooltips, turns off the interactive features:
Choose from multiple interactive highlighting effects:
Use Highlighted to emphasize specific points in a plot:
Presentation (17)
Multiple datasets are automatically colored to be distinct:
Provide explicit styling to different sets:
Label data with Callout:
Include legends for each curve:
Use Legended to provide a legend for a specific dataset:
Provide an interactive Tooltip for the data:
Use shapes to distinguish different datasets:
Use labels to distinguish different datasets:
Use Joined to connect datasets with lines:
Use InterpolationOrder to smooth joined data:
Show multiple sets in a row of separate panels:
Use a column instead of a row:
Plot the data in a stacked layout:
Plot the data as percentiles of the total of the values:
Use different axes for the different items:
Options (172)
ClippingStyle (6)
ClippingStyle requires at least one dataset to be Joined:
Omit clipped regions of the plot:
Show clipped regions like the rest of the curve:
Show clipped regions with red lines:
Show clipped regions as red at the bottom and thick at the top:
ColorFunction (6)
Use a color function to color points by their values:
Color by scaled ![]() and
and ![]() coordinates:
coordinates:
Color with a named color scheme:
Fill with the color used for the curve:
ColorFunction has higher priority than PlotStyle for coloring the curve:
Use Automatic in MeshShading to use ColorFunction:
ColorFunctionScaling (2)
DataRange (5)
Lists of height values are displayed against the number of elements:
Rescale to the sampling space:
Each dataset is scaled to the same domain:
Pairs are interpreted as ![]() ,
, ![]() coordinates:
coordinates:
Specifying DataRange in this case has no effect, since ![]() values are part of the data:
values are part of the data:
Filling (8)
Use symbolic or explicit values for "stem" filling:
Fill between corresponding points in two datasets:
Fill between datasets using a particular style:
Fill between datasets 1 and 2; use red when 1 is less than 2 and blue otherwise:
Fill to the axis for irregularly sampled data:
Use several irregular datasets; filling between them will use the first as the reference:
Joined datasets fill with solid areas:
The type of filling depends on whether the first set is joined:
FillingStyle (4)
Frame (3)
FrameLabel (4)
FrameTicks (9)
Frame ticks are placed automatically by default:
Use frame ticks on the bottom edge:
By default, the top and right edges have tick marks but no tick labels:
Use All to include tick labels on all edges:
Place tick marks at specific positions:
Draw frame tick marks at specified positions with specific labels:
Specify the lengths for tick marks as a fraction of the graphics size:
Use different sizes in the positive and negative directions for each tick mark:
Specify a style for each frame tick:
Construct a function that places ticks at the midpoint and extremes of the frame edge:
FrameTicksStyle (3)
ImageSize (1)
InterpolationOrder (5)
Joined lines can be interpolated:
By default, linear interpolation is used:
Use zero-order or piecewise-constant interpolation:
IntervalMarkers (3)
IntervalMarkersStyle (2)
Joined (4)
LabelingFunction (6)
By default, points are automatically labeled with strings:
Use LabelingFunction->None to suppress the labels:
Put the labels above the points:
Use callouts to label the points:
LabelingSize (4)
LabelingTarget (7)
Labels are automatically placed to maximize readability:
Use a denser layout for the labels:
Show the quarter of the labels that are easiest to read:
Only allow labels that are orthogonal to the points:
Only allow labels that are diagonal to the points:
Restrict labels to be above or to the right of the points:
MaxPlotPoints (1)
Mesh (6)
MeshFunctions (3)
MeshFunctions requires at least one dataset to be Joined:
Use a mesh evenly spaced in the ![]() and
and ![]() directions:
directions:
Show 5 mesh levels in the ![]() direction (red) and 10 in the
direction (red) and 10 in the ![]() direction (blue):
direction (blue):
MeshShading (7)
MeshShading requires at least one dataset to be Joined:
Alternate red and blue segments of equal width in the ![]() direction:
direction:
Use None to remove segments:
MeshShading can be used with PlotStyle:
MeshShading has higher priority than PlotStyle for styling the curve:
Use PlotStyle for some segments by setting MeshShading to Automatic:
MeshShading can be used with ColorFunction:
MultiaxisArrangement (5)
PlotFit (4)
Automatically fit a model to the data:
Fit a straight line to the data:
Fit a quadratic curve to the data:
Use KernelModelFit to approximate the data:
PlotFitElements (3)
PlotHighlighting (9)
Plots have interactive coordinate callouts with the default setting PlotHighlightingAutomatic:
Use PlotHighlightingNone to disable the highlighting for the entire plot:
Use Highlighted[…,None] to disable highlighting for a single set:
Move the mouse over a set of points to highlight it using arbitrary graphics directives:
Move the mouse over the points to highlight them with balls and labels:
Use a ball and label to highlight a specific point on the plot:
Move the mouse over the curve to highlight it with a label and droplines to the axes:
Use a ball and label to highlight a specific point in the plot:
Move the mouse over the plot to highlight it with a slice showing ![]() values corresponding to the
values corresponding to the ![]() position:
position:
Highlight a particular set of points at a fixed ![]() value:
value:
Move the mouse over the plot to highlight it with a slice showing ![]() values corresponding to the
values corresponding to the ![]() position:
position:
Highlight the curves at a fixed ![]() value:
value:
Use a component that shows the points on the plot closest to the ![]() position of the mouse cursor:
position of the mouse cursor:
Specify the style for the points:
Use a component that shows the coordinates on the points closest to the mouse cursor:
Use Callout options to change the appearance of the label:
PlotInteractivity (3)
PlotLabels (6)
Specify text to label sets of points:
Place the labels above the points:
Use callouts to identify the points:
Use the keys from an Association as labels:
Use None to not add a label:
PlotLayout (3)
PlotLegends (7)
No legend is used, by default:
Generate a legend using labels:
Generate a legend using placeholders:
Legends use the same styles as the plot:
Use Placed to specify the legend placement:
Place the legend inside the plot:
Use PointLegend to change the legend appearance:
PlotMarkers (8)
ListPlot normally uses distinct colors to distinguish different sets of data:
Automatically use colors and shapes to distinguish sets of data:
Change the size of the default plot markers:
Use arbitrary text for plot markers:
Use explicit graphics for plot markers:
PlotRange (2)
PlotStyle (7)
Use different style directives:
By default, different styles are chosen for multiple datasets:
Explicitly specify the style for different datasets:
PlotStyle applies to both lines and points:
PlotStyle can be combined with ColorFunction:
PlotStyle can be combined with MeshShading:
PlotTheme (2)
ScalingFunctions (9)
By default, plots have linear scales in each direction:
Use a log scale in the ![]() direction:
direction:
Use a linear scale in the ![]() direction that shows smaller numbers at the top:
direction that shows smaller numbers at the top:
Use a reciprocal scale in the ![]() direction:
direction:
Use different scales in the ![]() and
and ![]() directions:
directions:
Reverse the ![]() axis without changing the
axis without changing the ![]() axis:
axis:
Use a scale defined by a function and its inverse:
Positions in Ticks and GridLines are automatically scaled:
PlotRange and AxesOrigin are automatically scaled:
Applications (9)
Compare the n![]() prime to an estimate:
prime to an estimate:
Show the evaluation points in the order used by a numerical function:
Show both evaluation points and value used by a numerical function:
Plot life expectancy against birth rates for all the countries:
Show the linear relationship between enthalpy of vaporization and boiling point:
Plot a discrete-time signal and its spectrum:
Plot the probability mass function for a distribution:
Plot the empirical probability mass function:
Plot a solution sequence to a difference equation:
Properties & Relations (14)
By default pairs are interpreted as ![]() values:
values:
Interpret the data as multiple datai:
ListLinePlot is a special case of ListPlot:
Use Plot for functions:
Use ListLogPlot, ListLogLogPlot, and ListLogLinearPlot for logarithmic plots:
Use ListPolarPlot for polar plots:
Use DateListPlot to show data over time:
Use ComplexListPlot to plot complex numbers using their real and imaginary parts:
Use ListPointPlot3D to show three-dimensional points:
Use ListLinePlot3D to plot curves through lists of points:
Plot curves through rows of heights in a table:
Use ListPlot3D to create surfaces from data:
Use ListContourPlot to create contours from continuous data:
Use ListDensityPlot to create densities from continuous data:
Use ArrayPlot and MatrixPlot for arrays of discrete values:
Use ParametricPlot for parametric curves:
See Also
ListLinePlot DiscretePlot Plot ListLogPlot DateListPlot ListPolarPlot StackedListPlot ListPointPlot3D ListLinePlot3D ListPlot3D NumberLinePlot Graphics Point Fit
Function Repository: MultipleAxesListPlot
Tech Notes
Related Guides
-
▪
- Data Visualization ▪
- GPU Computing ▪
- Numbers with Uncertainty ▪
- Tabular Visualization ▪
- Discrete Calculus ▪
- Charting and Information Visualization ▪
- Scientific Data Analysis ▪
- Tabular Processing Overview ▪
- Tabular Communication ▪
- Signal Visualization & Analysis ▪
- Handling Arrays of Data ▪
- GPU Computing with NVIDIA ▪
- GPU Computing with Apple ▪
- Statistical Visualization ▪
- Numerical Data ▪
- Financial Visualization ▪
- Function Visualization ▪
- Associations ▪
- Spatial Point Collections ▪
- Probability & Statistics with Quantities ▪
- Audio Representation
Related Workflows
- Change the Style of Points in a 2D Scatter Plot
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2007 (6.0) ▪ 2008 (7.0) ▪ 2012 (9.0) ▪ 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2016 (10.4) ▪ 2016 (11.0) ▪ 2018 (11.3) ▪ 2019 (12.0) ▪ 2021 (13.0) ▪ 2023 (13.3) ▪ 2025 (14.2) ▪ 2025 (14.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), ListPlot, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ListPlot.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "ListPlot." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ListPlot.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). ListPlot. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ListPlot.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_listplot, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ListPlot}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ListPlot.html}", note=[Accessed: 12-December-2025]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_listplot, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ListPlot}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ListPlot.html}, note=[Accessed: 12-December-2025]}